Biden to Decide on $15B Nippon Steel Acquisition of U.S. Steel
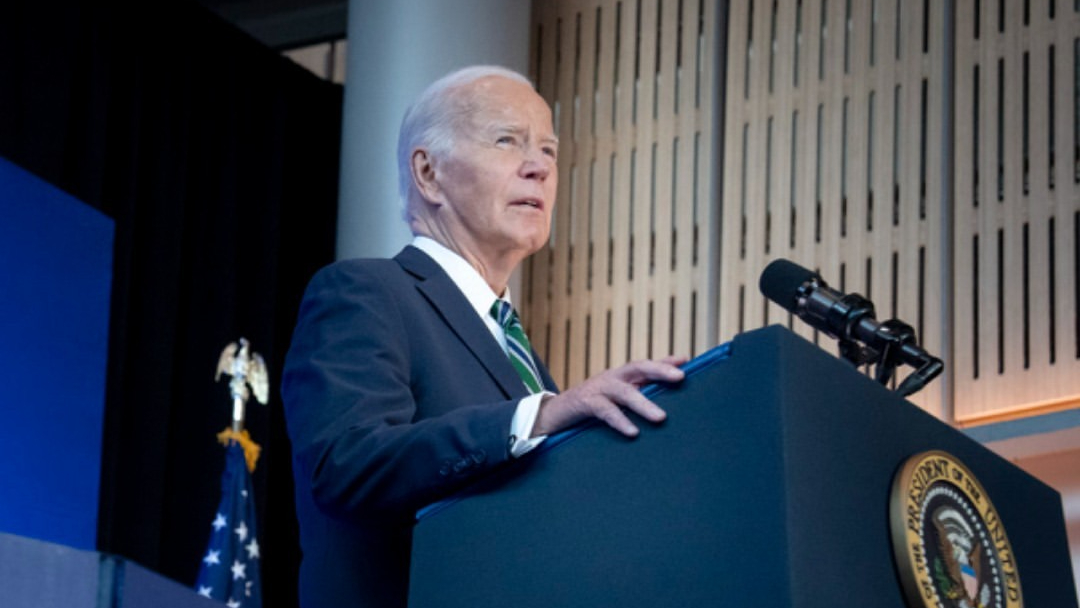
President Joe Biden is tasked with determining the fate of Nippon Steel's $15 billion bid to acquire U.S. Steel, a deal that has sparked fierce debates over its potential impact on national security, the American steel industry, and unionized labor. The Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States (CFIUS) has concluded its review, failing to reach a consensus and passing the decision to the President.
The Deal at a Glance
The proposed acquisition would make U.S. Steel a subsidiary of Nippon Steel, retaining its name and headquarters in Pittsburgh, the historic center of American steelmaking. This move would elevate the combined entity into the ranks of the world’s top three steel producers, according to the World Steel Association’s 2023 data.
Highlights of the deal include:
- $2.7 billion in investments into U.S. Steel’s facilities, including aging blast furnaces in Pennsylvania and Indiana.
- No layoffs or plant closures during the existing labor agreement.
- $5,000 closing bonuses for U.S. Steel employees, totaling nearly $100 million.
- Assurance of support in trade disputes and avoidance of importing competing steel slabs.
Despite these commitments, the deal faces staunch opposition from unionized workers, political figures, and industry advocates concerned about the implications of foreign ownership of a strategic American enterprise.
National Security Concerns
The CFIUS review, overseen by Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen, assessed whether foreign ownership of U.S. Steel poses risks to national security. While some agencies doubted the existence of significant risks, others remained cautious.
In September 2024, President Biden issued an executive order expanding CFIUS’s review criteria to include supply chain vulnerabilities and risks to Americans’ personal data. This deal is one of the first major tests under the enhanced guidelines.
Nippon Steel operates globally, with factories in the U.S., Mexico, China, and Southeast Asia, and is a key supplier for industries ranging from automotive to construction. Proponents of the deal argue that Nippon Steel’s robust financial position can help modernize U.S. Steel’s facilities, enhancing its competitiveness against Chinese steel producers, which dominate the global market.
Union and Political Opposition
The United Steelworkers union, representing U.S. Steel employees, strongly opposes the acquisition. The union has raised concerns about:
- The preservation of unionized jobs.
- Honoring collective bargaining agreements.
- Protecting American steel production from cheaper foreign imports.
Union president David McCall reiterated these points, urging President Biden to reject the deal. "We firmly maintain that this should involve keeping U.S. Steel under domestic ownership and management," McCall said.
President Biden and former President Donald Trump have both voiced their opposition. Trump has called for alternative measures to revitalize U.S. Steel, including tax incentives and tariffs, vowing to block the deal if re-elected.
Despite this, Nippon Steel has gained some support from union members near blast furnaces in Pennsylvania and Indiana, who see the company’s financial strength as a potential lifeline for U.S. Steel’s aging infrastructure.
Economic and Political Implications
The deal comes at a critical time for the American steel industry, which has benefited from protectionist tariffs and political support for revitalizing domestic manufacturing. In battleground states like Pennsylvania, the outcome could have significant implications for the 2024 presidential election.
Proponents of the deal emphasize its potential to strengthen domestic steel production, create jobs, and position U.S. Steel for future success. Critics, however, argue that foreign ownership could erode America’s industrial and economic sovereignty.
Related: Millions Could See Significant Boost in Social Security Benefits with Proposed Fairness Act
CFIUS’s Role and Next Steps
CFIUS, empowered by the 2018 Foreign Investment Risk Review Modernization Act (FIRRMA), has the authority to block transactions or impose conditions to mitigate risks. With no consensus reached, the decision now rests with President Biden, who has 15 days to rule on the matter.
Nippon Steel has made public assurances to address concerns, including pledges to:
- Maintain unionized employment.
- Refrain from importing competing products.
- Invest heavily in U.S. Steel’s facilities to ensure long-term competitiveness.
What’s at Stake
The outcome of this deal could reshape the landscape of the American steel industry, setting a precedent for foreign investments in critical sectors. It also underscores the challenges of balancing national security with economic growth in an era of globalized competition.
As President Biden deliberates, the decision will have far-reaching consequences for American workers, manufacturing, and trade policy, all while highlighting the complexities of protecting U.S. industries in a global economy.